| Drywood Termite |
 |
Family Rhinotermitidae
Characteristics
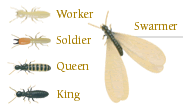
Size: Worker: 1/8- to 3/8-inch in length. Soldier: Body is similar to that of the worker, but large, deck head with powerful mandibles. Supplementary Reproductive: About one inch in length. Primary Reproductive: About one inch in length.
Colour: Worker: Pale, cream colored. Soldier: Light colored with brown head. Supplementary Reproductive: Light colored. Primary Reproductive: Dark brown/black.
Soldiers have an elongated head with pincer-like mandibles. Supplementary Reproductives have either no wings or very short non-functional wings, while Primary Reproductives have four wings of equal size until they are shed. Primary Reproductives are the termites most often seen in the open. They are commonly referred to as "swarmers."
Behaviour
This termite is known to swarm in spring, but small flights can occur at any
time of the year. Swarming is the visible means that termites use to establish
new colonies. As the colony grows, specialized castes are produced for the
different tasks required. One caste produced is the workers. Another caste is
the soldiers. And a third caste is the reproductives. Primary reproductives
swarm and start new colonies. They are called alates or swarmers. Although
thousands of primary reproductives may be produced each year, they all leave the
nest. Supplementary reproductives, on the other hand, can become reproductive
only in the colonies in whch they were born. They assit the primary king and
queen in population growth of the colony.
Habitat
Subterranean termites live in colonies in the ground, building vertical tunnels
that look like mud tubes above ground level so that they can search for food.
Because subterranean termites will die if exposed to air for an extended period
of time, the tunnels provide protection from the open air, allowing workers to
carry food to the nest. Subterranean termites can form tunnels through cracks in
concrete, so slab homes are not exempt from these termites. They need to stay in
contact with the soil in order to survive, unlike drywood termites that only
need low moisture.
Tips for Control
There are several things a homeowner can do which can help prevent termite infestations or make them easier to detect.
- Store wood away from the house.
- Make sure at least four inches of the foundation can be seen all around the home. Siding should not extend into the soil. Mulch and soil should not touch the siding.
- Make sure water drains away from the foundation to ensure water does not accumulate. Rain gutters are ideal; however, the downspout should direct the water away from the home.
- Roof or plumbing leaks can allow termites to survive above ground in a house. These should be corrected as soon as possible.
|